broadcast_to
- paddle. broadcast_to ( x: Tensor, shape: ShapeLike, name: str | None = None ) Tensor [source]
-
Broadcast the input tensor to a given shape.
Both the number of dimensions of
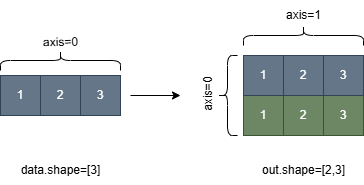
xand the number of elements inshapeshould be less than or equal to 6. The dimension to broadcast to must have a value 0.The following figure shows the process of broadcasting a one-dimensional tensor of shape [3] to a two-dimensional tensor of shape [2,3] based on the shape specified by ‘shape’.
Note
Alias Support: The parameter name
inputcan be used as an alias forx, andsizecan be used as an alias forshape. For example,broadcast_to(input=tensor_x, size=[2, 3], ...)is equivalent tobroadcast_to(x=tensor_x, shape=[2, 3], ...).- Parameters
-
x (Tensor) – The input tensor, its data type is bool, float16, float32, float64, int32, int64, uint8 or uint16. alias:
input.shape (list|tuple|Tensor) – The result shape after broadcasting. The data type is int32. If shape is a list or tuple, all its elements should be integers or 0-D or 1-D Tensors with the data type int32. If shape is a Tensor, it should be an 1-D Tensor with the data type int32. The value -1 in shape means keeping the corresponding dimension unchanged. alias:
size.name (str|None, optional) – Name for the operation (optional, default is None). For more information, please refer to api_guide_Name.
- Returns
-
N-D Tensor, A Tensor with the given shape. The data type is the same as
x.
Examples
>>> import paddle >>> data = paddle.to_tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype='int32') >>> out = paddle.broadcast_to(data, shape=[2, 3]) >>> print(out) Tensor(shape=[2, 3], dtype=int32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]])
