flip
- paddle. flip ( x: Tensor, axis: Sequence[int] | int, name: str | None = None ) Tensor [source]
-
Reverse the order of a n-D tensor along given axis in axis.
The image below illustrates how
flipworks.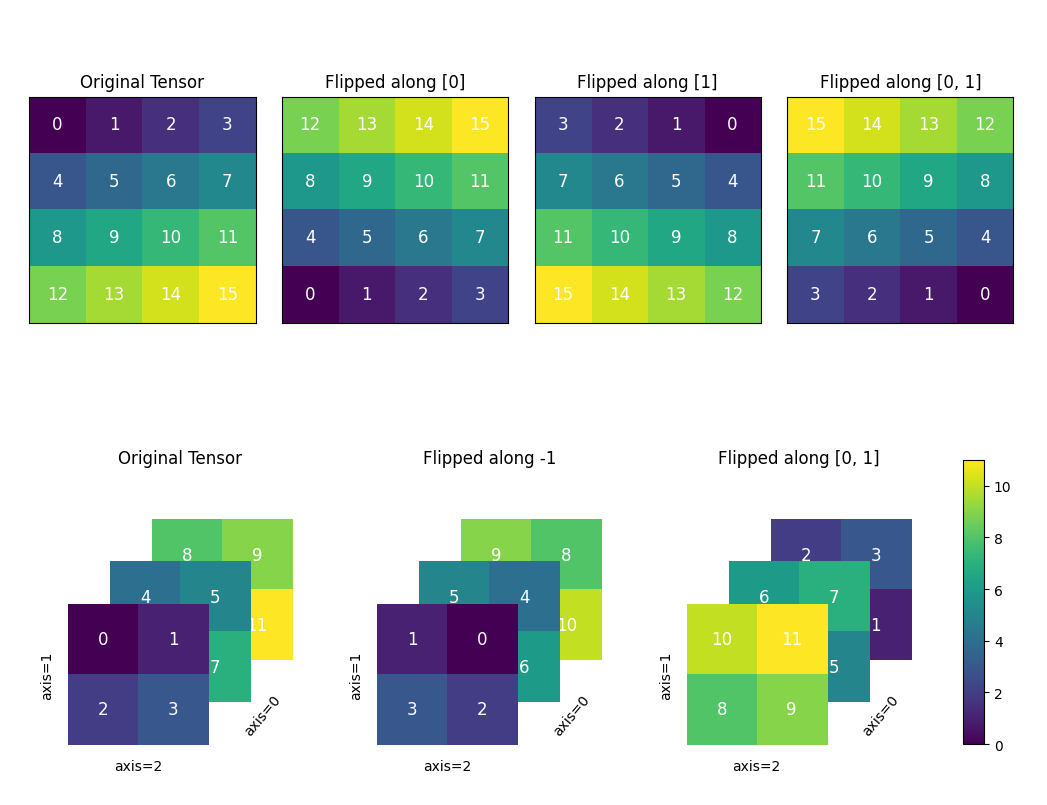
- Parameters
-
x (Tensor) – A Tensor with shape \([N_1, N_2,..., N_k]\) . The data type of the input Tensor x should be float32, float64, int32, int64, bool.
axis (list|tuple|int) – The axis(axes) to flip on. Negative indices for indexing from the end are accepted.
name (str|None, optional) – Name for the operation (optional, default is None). For more information, please refer to api_guide_Name.
- Returns
-
Tensor, Tensor or DenseTensor calculated by flip layer. The data type is same with input x.
Examples
>>> >>> import paddle >>> image_shape=(3, 2, 2) >>> img = paddle.arange(image_shape[0] * image_shape[1] * image_shape[2]).reshape(image_shape) >>> tmp = paddle.flip(img, [0,1]) >>> print(tmp) Tensor(shape=[3, 2, 2], dtype=int64, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [[[10, 11], [8 , 9 ]], [[6 , 7 ], [4 , 5 ]], [[2 , 3 ], [0 , 1 ]]]) >>> out = paddle.flip(tmp,-1) >>> print(out) Tensor(shape=[3, 2, 2], dtype=int64, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [[[11, 10], [9 , 8 ]], [[7 , 6 ], [5 , 4 ]], [[3 , 2 ], [1 , 0 ]]])
