stack
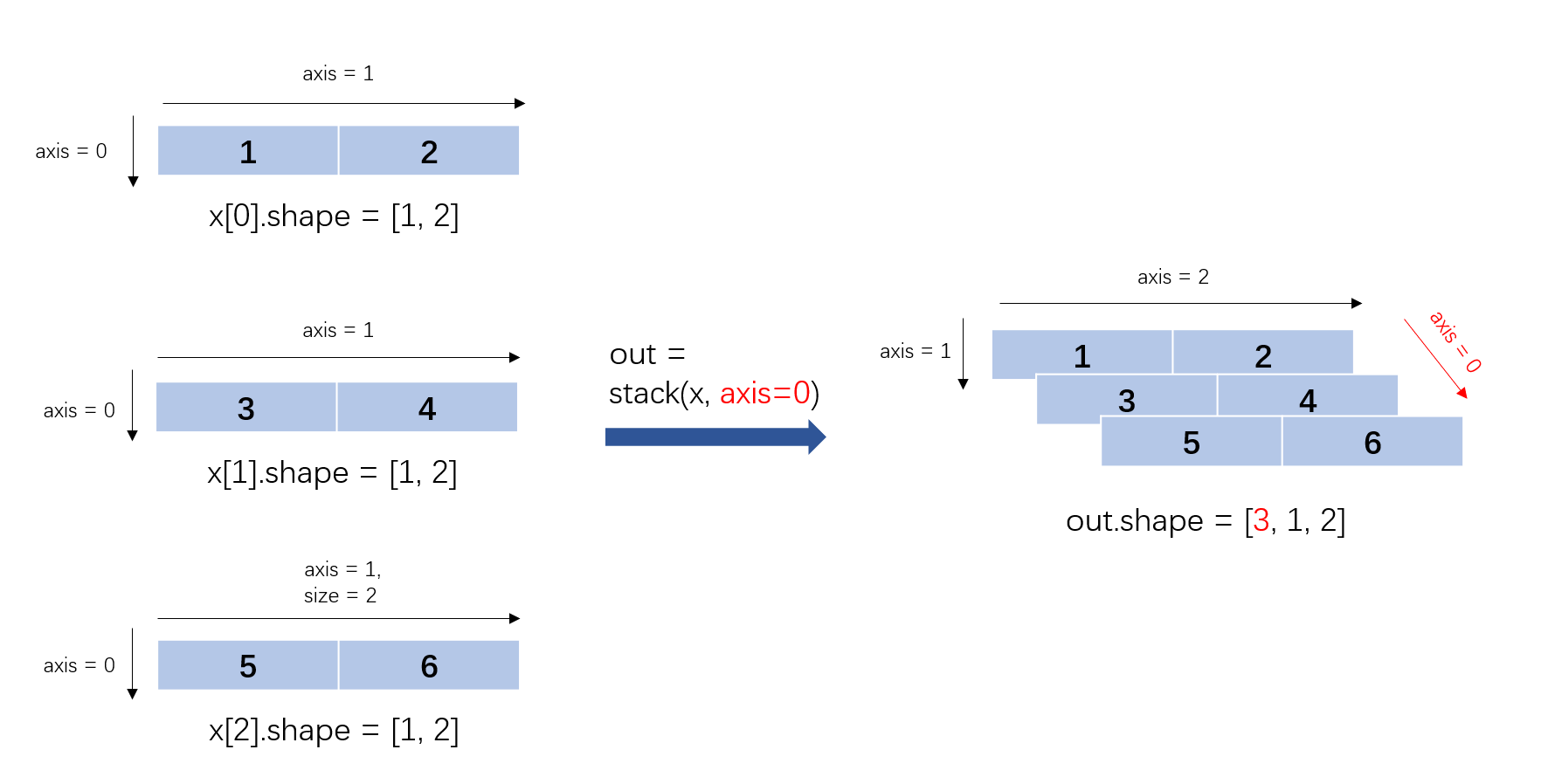
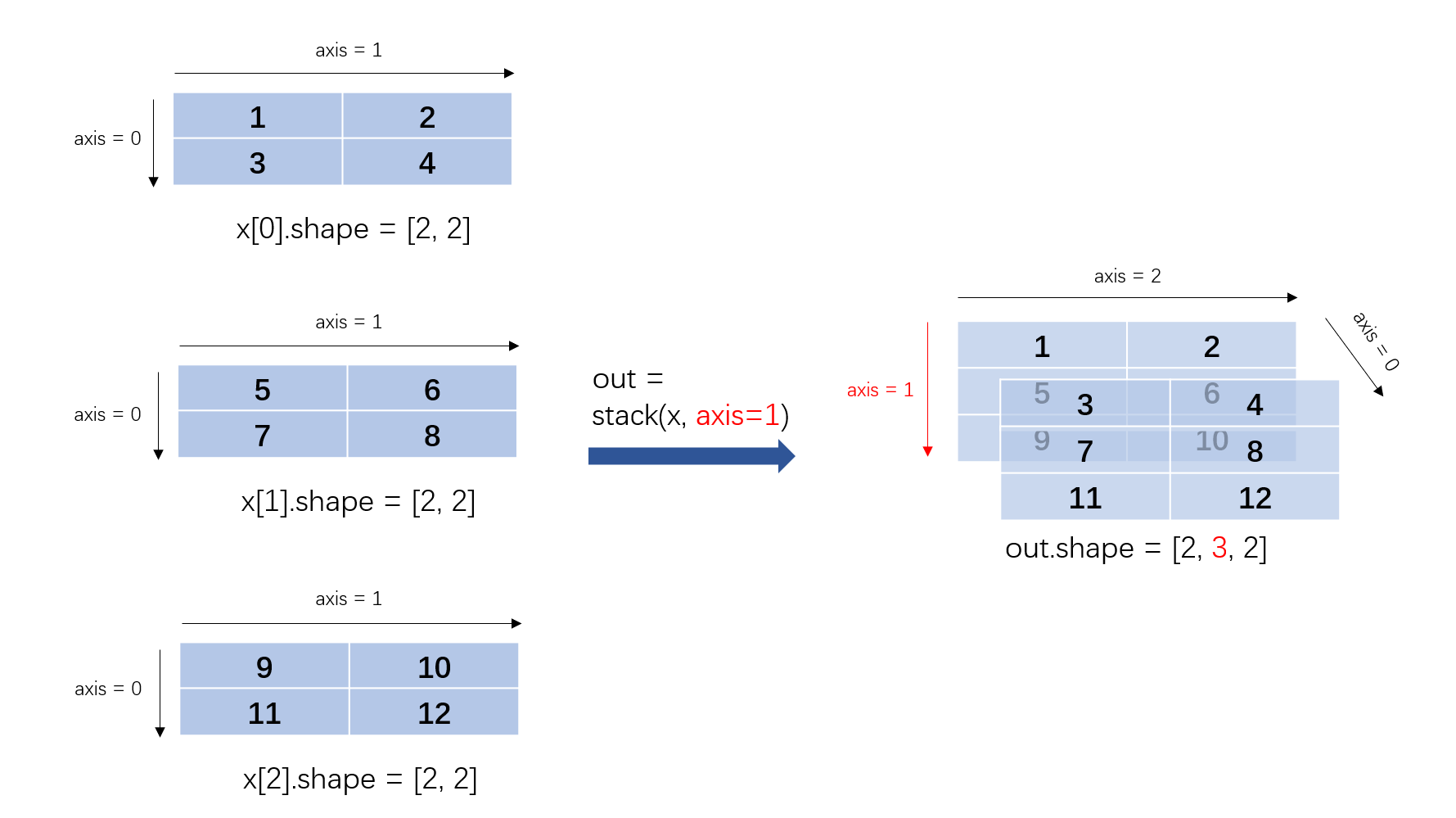
沿 axis 轴对输入 x 进行堆叠操作。要求所有输入 Tensor 有相同的 Shape 和数据类型。 例如,输入 x 为 N 个 Shape 为 [A, B]的 Tensor,如果 axis==0,则输出 Tensor 的 Shape 为 [N, A, B];如果 axis==1,则输出 Tensor 的 Shape 为 [A, N, B];以此类推。
Case 1:
Input:
x[0].shape = [1, 2]
x[0].data = [ [1.0 , 2.0 ] ]
x[1].shape = [1, 2]
x[1].data = [ [3.0 , 4.0 ] ]
x[2].shape = [1, 2]
x[2].data = [ [5.0 , 6.0 ] ]
Attrs:
axis = 0
Output:
Out.dims = [3, 1, 2]
Out.data =[ [ [1.0, 2.0] ],
[ [3.0, 4.0] ],
[ [5.0, 6.0] ] ]
Case 2:
Input:
x[0].shape = [1, 2]
x[0].data = [ [1.0 , 2.0 ] ]
x[1].shape = [1, 2]
x[1].data = [ [3.0 , 4.0 ] ]
x[2].shape = [1, 2]
x[2].data = [ [5.0 , 6.0 ] ]
Attrs:
axis = 1 or axis = -2 # If axis = -2, axis = axis+ndim(x[0])+1 = -2+2+1 = 1.
Output:
Out.shape = [1, 3, 2]
Out.data =[ [ [1.0, 2.0]
[3.0, 4.0]
[5.0, 6.0] ] ]
图解说明(一):
图解说明(二):
参数
x (list[Tensor]|tuple[Tensor]) – 输入 x 是多个 Tensor,且这些 Tensor 的维度和数据类型必须相同。支持的数据类型:float32、float64、int32、int64。别名
input。axis (int,可选) – 指定对输入 Tensor 进行堆叠运算的轴,有效 axis 的范围是:[−(R+1),R+1),R 是输入中第一个 Tensor 的维数。如果 axis < 0,则 axis=axis+R+1。默认值为 0。别名
dim。name (str,可选) - 具体用法请参见 api_guide_Name,一般无需设置,默认值为 None。
关键字参数
out (Tensor,可选) - 输出 Tensor,若不为
None,计算结果将保存在该 Tensor 中,默认值为None。
返回
堆叠运算后的 Tensor,数据类型与输入 Tensor 相同。
代码示例
>>> import paddle
>>> x1 = paddle.to_tensor([[1.0, 2.0]])
>>> x2 = paddle.to_tensor([[3.0, 4.0]])
>>> x3 = paddle.to_tensor([[5.0, 6.0]])
>>> out = paddle.stack([x1, x2, x3], axis=0)
>>> print(out.shape)
[3, 1, 2]
>>> print(out)
Tensor(shape=[3, 1, 2], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True,
[[[1., 2.]],
[[3., 4.]],
[[5., 6.]]])
>>> out = paddle.stack([x1, x2, x3], axis=-2)
>>> print(out.shape)
[1, 3, 2]
>>> print(out)
Tensor(shape=[1, 3, 2], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True,
[[[1., 2.],
[3., 4.],
[5., 6.]]])
>>> # zero-size tensors
>>> x1 = paddle.ones([0, 1, 2])
>>> x2 = paddle.ones([0, 1, 2])
>>> out = paddle.stack([x1, x2], axis=0)
>>> print(out.shape)
[2, 0, 1, 2]
>>> print(out)
Tensor(shape=[2, 0, 1, 2], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True,
[[],
[]])
>>> out = paddle.stack([x1, x2], axis=1)
>>> print(out.shape)
[0, 2, 1, 2]
>>> print(out)
Tensor(shape=[0, 2, 1, 2], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True,
[])